Different Network
Technologies
Layouts
Bus
Bus
is a network topology is generally used in Local Area Network. The bus topology
consist of single cable that carries all the traffic passing through. The
entire nodes are attached to a single leaner cable. The nodes can be
workstations, server and other devices. In a bus topology if data is sent, it
will then travel through the backbone line until it finds the right MAC or IP
address. If the machines do not match the intended address for the data then it
will reject the data until it find the right machine where the data has to be
sent. The drawback of this topology is if there is a fault in central lines,
then the whole network will eventually go down.
Star
Another
network topology and the reason why it’s called star, is because the layout is
identical as a star. A star topology is one of the most commonly used networks
set up in homes, offices or building. All the computer in the star topologies
is connected to the central device such hub, switch or router and if it
receives any message it tends to broadcast to all the computers. The good thing
about such topology is when a single system fails; it won't affect the other
but if the hub fails then the entire network will go down.
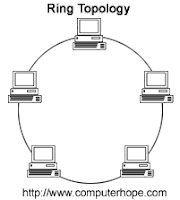
Ring
A
ring topology is a network within which all computers are connected in a circle.
Each computer in ring topology is attached in one single path. Ring topologies
use token ring in order to send the data from one machine to another until it
ends up where it started. Each node in the ring has a unique address for each
computer in the ring which means if the data is sent it will deliver the data
to the correct computer that have been requested. The purpose of having node in
the ring topology is to handle every data packets that have been sent. There
are nodes in the ring topology which means if a data is sent then the data will
go from one node to the next node in a circle which means the data will flow in
a single direction. In the Ring topology, if one computer goes down, the whole
topology will go down too.
Mesh
Another
network topology where each of the nodes is interconnected with each other as
shown in the above picture. In mesh topology, if one of the connections goes
down, nothing will happen and the transmitting of data will still carry. Such
topology is a lot expensive and complicated and it’s not largely used for most
of the networks available. However, this topology is usually utilised for
wireless network due to its complexity.
Tree
A
network topology with a combination of Bus and Star network topologies. The
structure of such topology is identified to a tree therefore it facilitates
users to have numerous servers on the actual network. In addition to that, you
can divide the network in various ways. This topology is commonly used in
colleges and schools as each of the divided parts can recognise related systems
in their own network and nevertheless connected to the largest network in some
way.
Hybrid
A
similar to tree topology which has combinations of two network topology. This
topology connects network part by linking the features of two or more network
topology such as bus, star, ring and token ring. The purpose of such topology
is to keep up consistency for different task. This particular topology is much
more reliable than others as it professionally can identify faults and isolate
them as quickly as possible.
Devices
Routers
Routers
are designed to handle the paths along which the data is transmitted within a
network. Routers are significant piece and essentials for an easy communication
between the internet and the computer. The internet data are transmitted
through TCP/IP Protocols which are created to communicate data. As soon as the
data is transferred, it tends to divide the data into packet therefore the
router is configured to direct these data packet to its intended destination
through best possible route.
Switches
An
essential piece hardware as it is designed to accelerate thing up. Switches
facilitate different computer on a network to communicate directly with one
another in a smooth and in a professional manner. The switches main job is to
filter and forward data packets among LAN section. It functions at layer 2 of
the OSI model. The switch doesn’t look at IP address information however, it
only looks for Ethernet MAC addresses and keeps a table of all MAC addresses
passing through the switch. The reason why the switch is considered as “clever”
is because it just transmits data to the device that are destined for that
which saves bandwidth. In the other hand, the hub is considered as “dumb”
because it broadcasts the data to every device connected and that technique
causes more collision to occur.
NICs
NIC
stands for Network Interface Card that is attached in PC so it can allow the
connection to a network. It is used in LAN transmission technology such as
token ring or Ethernet, enabling a system to connect to and communicated via a
network. Network Interface Card provides full time connection to a network.
Most hone and portable computer connects to the internet via dial up
connection.
Server
Computer
servers are used to store, retrieve and transfer files and data to another
location on its network or the internet. The server is designed to carry
multiple tasks therefore they have additional processing power and storage
capacity in order to handle loads of users that utilises the network. There are
various types of server designed such as web server, print server, file server,
database server and so on so forth.
Proxy
A
proxy is a device that acts as a server. It is located between a client application
(web browser) and an actual server. It intercepts every single request to the
actual server in order to see if it can complete the request itself. If not
successful then it forwards the request to the actual server.
Repeater
A
repeater is a device that is used in the network in order to regenerate or
duplicate a signal. The repeater is mostly used in communication systems to
regenerate digital or analogue signals distorted by transmission loss. Analogue
repeater frequently can make the signal stronger while digital repeaters can
rebuild signal almost identical as the actual quality.
Bridge
The
bridge is also a device designed to be used in the network. The bridge is
designed to connect two parts of a network together at the data link layer of the
OSI model. Bridges functions in the same as the switch does however, the data
traffics are handled in a different way. A bridge itself will only transmit
traffic from one side to the other if it is going to a destination on the other
side.
Protocols
TCP/IP
TCP
stands for transmission control protocol and IP stands for internet protocol.
TCP/IP is very important part of the internet and it's composite. LAN, WAN and
other network types utilises such protocol as its ability to transmit packets
from any computer system, regardless of network uniqueness and operating system
differences. It provides a communication service at an intermediate level
between an application program. This can also be used as an intranet or a
private network and when you would like to set up a direct access to the
internet, the computer is offered with a copy of the TCP/IP program similar to
any other computer which may send to or else get information from as well as a
copy of TCP/IP. Because of TCP/IP, the users can connect to other users and
create communication such as send, receive and shared information throughout.
SNMP
SNMP
stands for Simple Network Management Protocol which is a set of protocols for
complex network which works by sending messages to different parts of the
network. Devices like router, server, switches, workstation printers modems
other are able to support SNMP protocol. The SNMP makes easy of the exchange of
management information between network devices. SNMP allows network managers to
handle network performance which includes finding and resolving network
problems that may occur time to time.
IPv4
The
IPv4 stand for Internet Protocol Version 4 which is the fourth modification of
the first internet protocol. IPv4 is used to recognise devices on a network
through an addressing system. It is the most commonly deployed internet
protocol used to connect devices to the internet.
IPV6
The
IPv6 is the sixth medications and the latest version of internet protocol. This
internet protocol enables more users and devices to communicate on the internet
by using a greater number to produce IP addresses. The IPv6 is also known as
the next generation internet because of its greater capabilities as well as its
expansion through large scale use.
DNS
DNS
stand for Domain Name System which is a naming system for services and
computer. The DNS is mainly responsible to link a variety of information with
domain names allocated to each of the individuals. The main profession of DNS
is the translation human language into a form of binary.
ARP
ARP
stands for Address Resolution Protocol which is an intent net protocol and
mainly it is used to convert an IP address into a physical address such as
Ethernet address. For example a host requiring getting a physical address it
tends to transmit an ARP request onto the TCP/IP network. The host on the network
that has the IP address in the request then responds with its physical address.
IPX
IPX
stand for Internetwork Packet Exchange and it is a protocol used to connect
networks by operating systems such as the Novell’s NetWare. The IPX is known as
connectionless, which means it doesn’t require connections to be maintained
throughout the exchange of packets. It can just pick up where it left off when
a connection is down.
Network O/S
Windows Server 2008
From
what I have researched, the Windows Server 2008 seems to be the second line of
operating system due to recent Windows Server released by Microsoft. The
windows server is designed from the same code as compared to Windows Vista. As
a result, it shares most of the similar functions as well as design. Due to the
similar code, it automatically comes with most of the security features and
administrative functions and features new to Windows Vista such as the
installation, monitoring, improved GUI and based installation so on and so
forth.
Linux Mandriva
A
Linux Mandriva operating system is available for individual and business for
free. As Linux Mandriva operating system is stable and secure, it’s great for
storing massive database of information. Linux is based on UNIX which is still
used currently just to run the internet. Linux is used both to run parts of the
internet and run a small and large network of offices and homes. Security wise
the Linux is much stronger than windows and does not require an antivirus to be
installed. Linux is seamless for old PCs with hardly any processing power or
memory.
Novell NetWare
A
Novell Netware is a network operating system which is used to provide
applications, files and peripheral network services to computers. Novell
Netware operating system is extremely powerful however, the downside is that
the operating system is based on difficult command strings and utilities.
Netware identifies the top five layers of the OSI model and runs on virtually
any media access protocol.